Tab Mapper
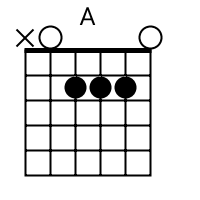
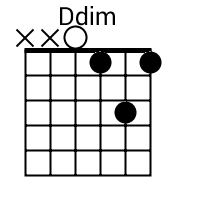
The tab mapper is a handy little tool that will render a guitar tab file with graphic chord diagrams displayed alongside. This comes in handy for people who just don't have every single chord shape memorized. Just plug in the web site address of a valid .tab or .crd file and hit "Go". In general, the tab mapper does a better job with printer friendly URLs. If there is more than one way to play a chord, the tab mapper will choose the most common shape. To see other fingerings, click on the chord diagram and you will be taken to the chord calculator.
Original file located @ http://e-cep.org.
Show me scales that sound good with the chords in this song: A, Do.
- Home
- Sitemap
- Contact Us
- TOPICS
- Adolescence Medicine
- Allergy
- Cardiology
- Critical Care Medicine
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Gastroenterology
- General Pediatrics
- Genetics and Metabolism
- Hematology
Browse all articles >
- Infection
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Neurology
- Nutrition
- Oncology
- Neurobehavior
- Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Other
- ARTICLE CATEGORY
- Perspective
- Review article
- Systematic review and meta-analysis
- Editorial
- Present Perspective on the Past Research
- Original article
- Letter to the editor
- Clinical note
- Case report
- Others
Browse all articles >
- BROWSE ARTICLES
- Current issue
- All issues
- Accepted articles
- Ahead-of print
- Most viewed
- Most downloaded
- Most cited
- Funded articles
- Search
- Author index
- FOR CONTRIBUTORS
- Instructions for authors
- Research and publication ethics
- Instructions for peer reviewers
- Author?s checklist
- Best article award
- Best reviewer award
- E-submission
- Copyright transfer agreement
- ABOUT
- Aims and scope
- About the journal
- Editorial board
- Best practice
- Open access
- Subscription information
- Contact us
-
Search
| Article 69(3); Mar 2026 |
| Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) effectively treat acid-related disorders, including gastroesophageal reflux disease, eosinophilic esophagitis, peptic ulcers, and Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. Long-term use, particularly in children, may lead to microbiome alterations, nutrient deficiencies, infections, renal injury, osteoporosis, fractures, and other gastrointestinal changes. PPI therapy should be guided by clear clinical indications, prescribed at the lowest effective dose for the shortest necessary duration, and regularly reassessed to minimize risks in young children. |
- Full text
- PubReader
- ePub
| Kawasaki disease (KD) is an acute febrile vasculitis and the leading cause of acquired heart disease in children. Despite decades of research, the etiology remains unknown and key mechanisms linking systemic inflammation to coronary artery lesions are incompletely defined. High-throughput technologies?including genomics, transcriptomics, proteomics, metabolomics, epigenomics, and immunomics?have enabled systems-level profiling of KD and highlighted reproducible inflammatory and vascular pathways.... |
- Full text
- PubReader
- ePub
| The definition of bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) has continued to evolve. Recently, newer definitions based on respiratory support at 36 weeks? postmenstrual age better predict long-term outcomes but diagnose BPD relatively late. To address this limitation, the New Japanese Classification uses early postnatal factors, including small for gestational age and bubbly or cystic chest radiographic findings, to predict severe BPD and enable early targeted interventions. |
- Full text
- PubReader
- ePub
| Question: Do gut microbiota differ between patients with Hirschsprung disease (HSCR) and healthy children, and can specific bacterial taxa predict postoperative HSCRassociated enterocolitis (HAEC)? Finding: Patients with HSCR showed gut dysbiosis with reduced diversity. Postoperative microbial changes included increased alpha diversity. Certain taxa, such as Eubacterium and Collinsella, were associated with recovery or HAEC. Meaning: Distinct microbial signatures may help identify HAEC risk and guide microbiota-based strategies to improve outcomes. |
- Full text
- PubReader
- ePub
| Question: Does completing a third-generation cephalosporin course, despite in vitro resistance, increase the early urinary tract infection recurrence rate in children? Finding: Among 989 Korean children, discordant therapy increased the 2-month recurrence risk by 40% compared with concordant or susceptible therapy. Meaning: Checking isolate susceptibility and switching to an active oral drug may curb recurrence and limit the use of broad-spectrum antibiotics. |
- Full text
- PubReader
- ePub
| Question: Does granulocyte transfusion improve survival and clinical recovery in pediatric febrile neutropenia? Finding: In this 15-year real-world cohort, granulocyte transfusion significantly increased 30-day survival (92.3 % vs. 65.4%; adjusted odds ratio, 0.105; P=0.020) and accelerated fever and neutrophil recovery without serious adverse events. Meaning: Granulocyte transfusion may be an effective adjunctive therapy for severe neutropenic infections in children, particularly in low- and middle-income settings. |
- Full text
- PubReader
- ePub
| Question: How does obesity severity affect baseline fitness and improvements in key obesity-related measures following participation in a structured lifestyle modification program? Finding: Severely obese youth showed poorer baseline physical fitness but greater improvements in key obesity-related measures following lifestyle interventions. Meaning: Early targeted intervention may help prevent progression to more severe obesity and declines in physical fitness in patients with obesity. |
- Full text
- PubReader
- ePub
| Question: Can a basophil activation test (BAT) of cord blood predict a cow's milk allergy? Finding: Infants with a high casein-BAT value were more likely to develop food allergy symptoms in the first year, whereas cow?s milk BAT showed no predictive association. Meaning: Cord blood casein BAT may help identify newborns at increased risk for early-life food allergies, enabling closer monitoring and preventive strategies, although larger studies are needed for validation. |
- Full text
- PubReader
- ePub
| Question: What are the characteristics and clinical implications of thrombocytopenia in preterm neonates born to mothers with systemic lupus erythematosus? Finding: Nearly one-third of preterm infants developed thrombocytopenia. Key modulators of this risk included gestational age, maternal hypertensive disorders of pregnancy, and hydroxychloroquine use. Thrombocytopenia may be associated with neonatal morbidity. Meaning: Platelet count should be monitored during the first week of life, and infants should be assessed for potential complications. |
- Full text
- PubReader
- ePub
| Question: Can the revised Japanese classification predict severe bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD) early in preterm infants? Finding: Small for gestational age and bubbly/cystic chest radiographic patterns were independently associated with severe BPD, and subtypes I and III showed particularly strong associations. Meaning: This classification may facilitate early risk stratification and guide timely supportive strategies to prevent progression to severe BPD. |
- Full text
- PubReader
- ePub
-
6.02024CiteScore98th percentilePowered by
-
Impact Factor3.6
- MOST CITED ACCEPTED ARTICLES
Cited By
40Prevalence of anxiety, depression, and stress among parents of neonates admitted to neonatal intensive care unit: a systematic review and meta-analysis Cited By
29Microplastic and human health with focus on pediatric well-being: a comprehensive review and call for future studies Cited By
29Community-acquired pneumonia in children: updated perspectives on its etiology, diagnosis, and treatment Cited By
25Metabolic complications of obesity in children and adolescents Cited By
20Development of orphan drugs for rare diseases +more
Authors? reply: a commentary on ?Assessing kidney outcomes in childhood-onset lupus nephritis: role of National Institutes of Health-modified histological indices? A commentary on ?Assessing kidney outcomes in childhood-onset lupus nephritis: role of National Institutes of Health-modified histological indices? Value of demographic factors in early identification of pediatric malignant vasovagal syncope in head-up tilt test Effects of induction-phase acute kidney injury and age at diagnosis on chronic kidney disease in pediatric acute lymphoblastic leukemia: a time-to-event cohort study Context-dependent features of transcriptomic landscapes in pregnant mother-neonate dyads of preeclampsia +more
- Adolescence Medicine
- Allergy
- Cardiology
- Critical Care Medicine
- Developmental and Behavioral Medicine
- Emergency Medicine
- Endocrinology
- Gastroenterology
- General Pediatrics
- Genetics and Metabolism
- Hematology
Browse all articles >
- Infection
- Neonatology (Perinatology)
- Nephrology (Genitourinary)
- Neurology
- Nutrition
- Oncology
- Neurobehavior
- Pulmonology
- Rheumatology
- Other
- Perspective
- Review article
- Systematic review and meta-analysis
- Editorial
- Present Perspective on the Past Research
- Original article
- Letter to the editor
- Clinical note
- Case report
- Others
Browse all articles >
BROWSE ARTICLES- Current issue
- All issues
- Accepted articles
- Ahead-of print
- Most viewed
- Most downloaded
- Most cited
- Funded articles
- Search
- Author index
- Instructions for authors
- Research and publication ethics
- Instructions for peer reviewers
- Author?s checklist
- Best article award
- Best reviewer award
- E-submission
- Copyright transfer agreement
- Aims and scope
- About the journal
- Editorial board
- Best practice
- Open access
- Subscription information
- Contact us
#1606 Seocho World Officetel, 19 Seoun-ro, Seocho-ku, Seoul 06732, Korea
Tel: +82-2-3473-7306 Fax: +82-2-3473-7307 E-mail: office@e-cep.org
Clinical and Experimental Pediatrics is an open access journal. All articles are distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/)
Copyright © 2026 by Korean Pediatric Society.